Give wings to your dreams and ambitions with a highly qualified team, amicable work environment, ample learning opportunities, and make your career graph rise exponentially.
Nano Therapeutics Pvt Ltd has been an out & out fan of skills and talent. The company always seeks scientific, administrative and finance wizards that can help the brand scale greater heights by pitching in innovative design ideas & creating out of the box sales/marketing strategies. Nano therapeutics firmly believes in the saying- “no global revolution stems from an individual.” At Nano Therapeutics each employee is an integral part of the success story of the company. The company believes in not just giving jobs but in making careers.
If you possess adept knowledge, vivid imagination, team-spirit & an inclination towards reshaping the face of clinical therapies, Nano Therapeutics Pvt Ltd’s doors are always open for you. Just send in your updated CV at hr@nano-therapeutics.net
About the size of our fist, heart is the most vital organ which supplies blood to every part of the body. Human heart is comprises of four chambers, Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Left Atrium and Left Ventricle. Right side of the heart receives blood which is low in oxygen from the veins all over the body, and pumps blood through pulmonary artery in the lungs where it is re-oxygenated. Whereas, the left side of the heart receives this oxygen rich blood from the lungs and then through Aorta (the body's main artery) this oxygen rich blood is pumped to other parts of the body by a complex network of arteries, arterioles and capillaries. The oxygen rich blood supplies essential nutrients to different body tissues while picking up carbon dioxide and other waste material from them. This deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium of the heart and the entire cycle begins again.
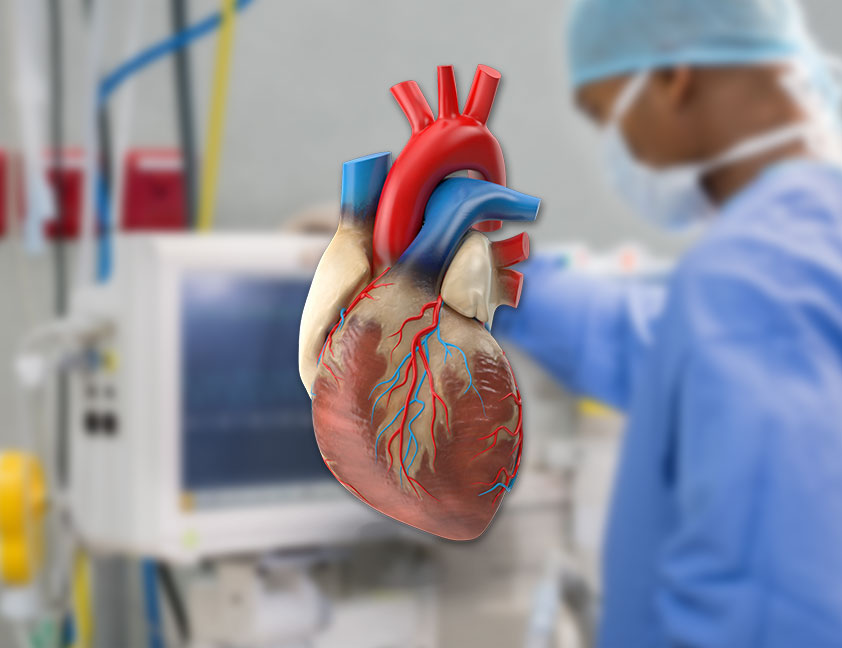
The heart is composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue that continuously contracts and relaxes, so it must have a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. The coronary arteries are the network of blood vessels that carry oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the cardiac muscle tissue.
Two coronary arteries, referred to as the "left" and "right" coronary arteries, emerge from the beginning of the aorta, near the top of the heart. The initial segment of the left coronary artery (LAD) is called the left main coronary. It branches into two slightly smaller arteries: the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery and the left circumflex coronary artery.
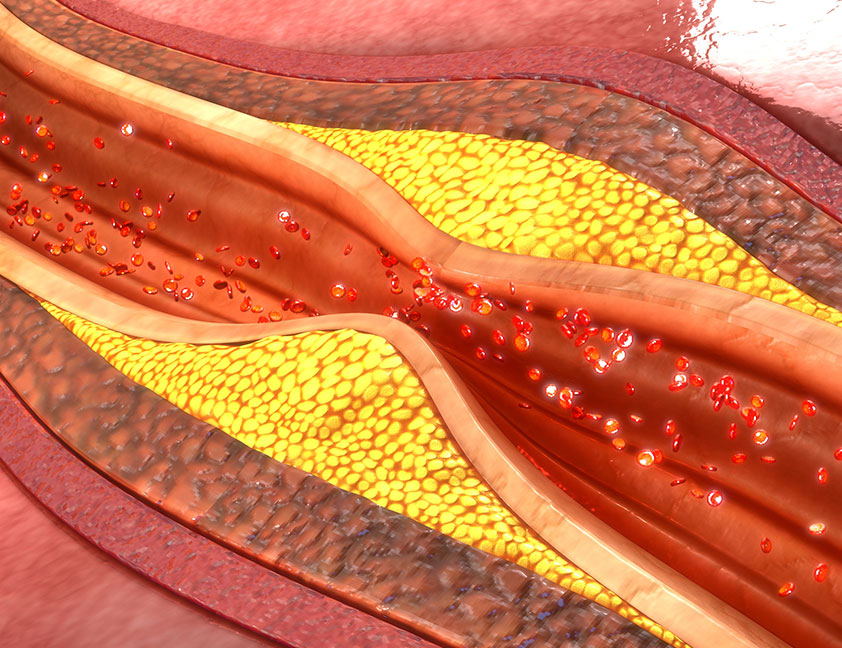
Coronary Artery Disease is an ailment in which the coronary arteries get clogged by fatty deposits know as "Plaque". Coronary arteries are the major arteries that supply blood, oxygen and nutrients to the heart. If fat build up occurs in one or more of the coronary arteries then it may result in Heart Attack. This may even cause Angina or Chest pain due to insufficient supply of blood/oxygen to the heart muscles. The Plaque deposited on the interior wall of coronary arteries may rupture and can lead to blood clotting. If the clot becomes large enough, it can block the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the portion of heart muscle fed by the artery. Blocked blood flow to the heart muscle ultimately causes a heart attack.
PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty)
What is percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) opens blocked coronary arteries caused by coronary artery disease (CAD) and restores arterial blood flow to the heart tissue without open heart surgery. (Percutaneous means through the skin), (Transluminal means in the channel or lumen of a blood vessel)
Angioplasty physically opens the channel of diseased arterial segments, relieves the recurrence of chest pain, increases the quality of life and reduces other complications of the disease. The blockage is due to deposition of fatty material within the walls of the arteries. This buildup causes the inside of the arteries to become rough and narrowed, limiting the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
How does the procedure works?
Before the Procedure
After the Procedure
Bed rest may vary from two to six hours depending on your specific condition. You may be given medication for pain or discomfort related to the insertion site or having to lie flat and still for a prolonged period. You will be encouraged to drink water and other fluids to help flush the contrast dye from your body.